DTW (Dynamic Time Warping)
DTW最初用于识别语音的相似性,当前DTW算法常用于计算两个时间序列的相似性,尤其适用于不同长度、不同节奏的时间序列 ## 算法流程 假设有两个序列 \[\mathbf{X}=\{\mathbf{x}_1,\mathbf{x}_{2},\ldots,\mathbf{x}_{n}\} \]
\[\mathbf{Y}=\{\mathbf{y}_1,\mathbf{y}_{2},\ldots,\mathbf{y}_{m}\}
\] 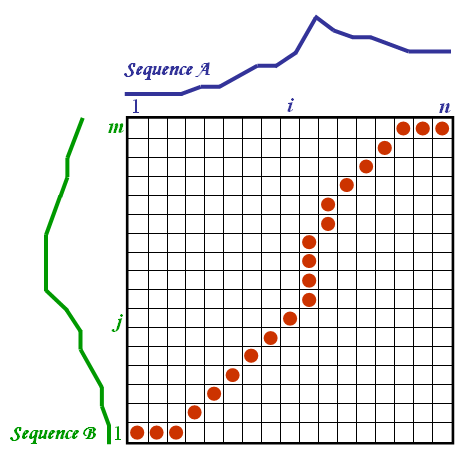
首先构建一个\(m\times n\)的二维数组\(W\),数组中每个点\(W(i,j)\)表示\(\mathbf{X}_{i}\)和\(\mathbf{Y}_{j}\)之间的累计距离\(\sqrt{ (\mathbf{X}_{i}-\mathbf{Y}_{j})^2 }\)。DTW的核心思想是在这样的一个距离矩阵中从两个序列的起点找到通往两个序列终点的最小距离路径,但是在寻找路径的过程中,必须满足一些约束条件: 1. 边界条件:起点必须是 \(w(1,1)\) ,终点必须是 \(w(1,1)\),要有始有终; 2. 连续性:意思是下一个满足条件的灰色方块一定是在当前灰色方块的周围一圈; 3. 单调性:下一个满足条件的灰色方块一定在当前灰色方块的右上方,不能回头; 假设有两个序列\(\mathbf{X}=\{1,3,2,4,2\}\),\(\mathbf{Y}=\{0,3,4,2,2\}\),根据欧氏距离可以直接计算得到两个序列之间的距离为: \[ dis = \sqrt{ (1-0)^2+(3-3)^2+(2-4)^2+(4-2)^2+(2-2)^2 }=\sqrt{ 5 } \]
构建距离累计\(w\)矩阵: 1. 首先构建最左边的一列,\(W(i,0)=dis(\mathbf{X}_{i}-\mathbf{Y}_{0})+W(i-1,0)\) 2. 然后构建最下边一行:\(W(0,j)=dis(\mathbf{X}_{0},\mathbf{Y}_{j})+W(0,j-1)\) 3. 最后构建表格中间的元素:\(W(i,j)=dis(\mathbf{X}_{i},\mathbf{Y}_{j})+\min(W(i-1,j),W(i,j-1),W(i-1),W(j-1))\) 4. 然后根据构建的距离累加矩阵从右上角到左下角寻找配准路径,寻找左下三个点钟较小的那个作为下一个节点 5. 最后得到配准的结果\(\{(\mathbf{x}_{1},\mathbf{y}_{1}), (\mathbf{x}_{2},\mathbf{y}_{2}),(\mathbf{x}_{3},\mathbf{y}_{2}),(\mathbf{x}_{4},\mathbf{y}_{3}),(\mathbf{x}_{5},\mathbf{y}_{4}),(\mathbf{x}_{5},\mathbf{y}_{5})\}\)
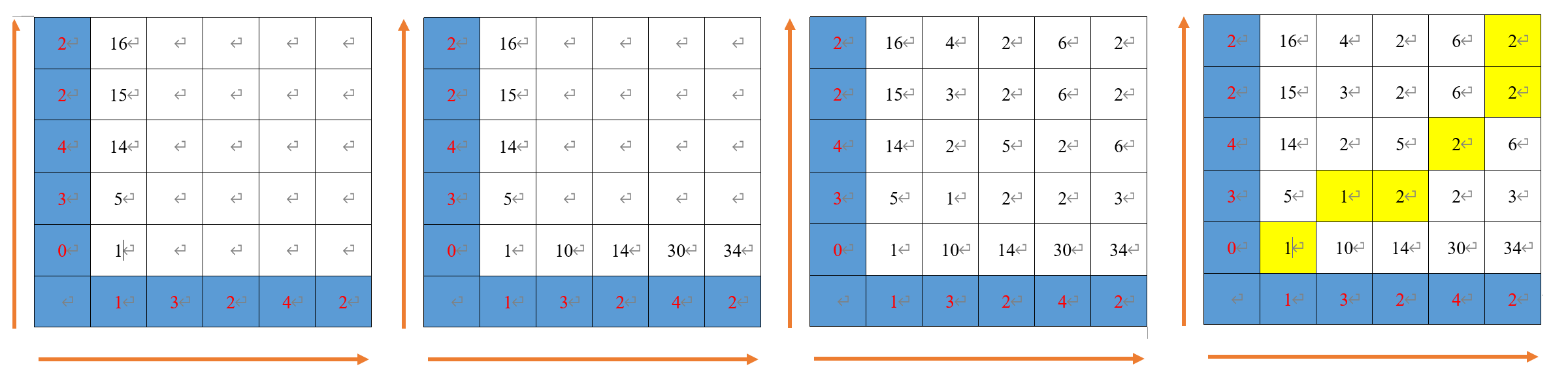
代码实现
1 | |